Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
| Catalog Number | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|
| LS-C58307-0.2 | 0.2 mg (1 mg/ml) | $486 |
Monoclonal Mouse anti‑Human S100 Protein Antibody (clone 6G1, WB) LS‑C58307
Monoclonal Mouse anti‑Human S100 Protein Antibody (clone 6G1, WB) LS‑C58307
Antibody:
S100 Protein Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (6G1) Antibody
Application:
WB, ELISA
Reactivity:
Human
Format:
Unconjugated, Unmodified
Toll Free North America
 (800) 227-6666
(800) 227-6666
For Research Use Only
Overview
Antibody:
S100 Protein Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (6G1) Antibody
Application:
WB, ELISA
Reactivity:
Human
Format:
Unconjugated, Unmodified
Specifications
Description
S100 Protein antibody LS-C58307 is an unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody to human S100 Protein. Validated for ELISA and WB.
Host
Mouse
Reactivity
Human
(tested or 100% immunogen sequence identity)
Clonality
IgG1
Monoclonal
Clone
6G1
Conjugations
Unconjugated
Purification
Affinity purified
Modifications
Unmodified
Immunogen
Human brain S100 protein.
Specificity
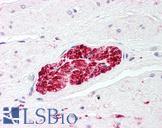
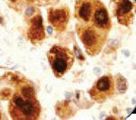
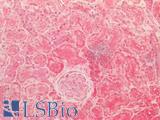
Recognizes S100 protein derived from human brain tissue. It is a 21kD acidic calcium-binding protein synthesized by astroglial cells. It can be found predominantly as two isoforms, the alpha-beta heterodimer (S100a) and the beta-beta homodimer (S100b). The S100 family of proteins have been implicated in a large variety of intracellular and extracellular regulatory activities, such as cellular energy metabolism, cytoskeleton modification, cell proliferation and differentiation. When glial cells are damaged, S100 protein is leaked into the extracellular matrix and cerebrospinal fluid, further releasing into the bloodstream. As such, S100 protein can be used as a sensitive and reliable marker for nervous system damage, such as after brain damage or acute stroke. Recognizes both S100a (alpha-beta) and S100b (beta-beta). May be used to detect S100 protein in ELISA assay. Sensitive to EDTA and other bivalent-binding agents. Better performance can be obtained in the presence of 5 mM CaCl2 in assay buffers.
Applications
- Western blot
- ELISA
Usage
ELISA: This product may be used in an indirect ELISA or as a detection antibody in a sandwich ELISA together with LS-C58309 as a capture reagent.
Presentation
PBS, 0.09% Sodium Azide
Storage
Store at 4°C or at -20°C. Store undiluted. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Microcentrifugation recommended if solution contains precipitate.
Restrictions
For research use only. Intended for use by laboratory professionals.
Publications (0)
Customer Reviews (0)
Featured Products
Species:
Bovine
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, Western blot, ELISA
Species:
Bovine
Applications:
IHC - Paraffin, IHC - Frozen
Species:
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications:
IHC, IHC - Paraffin, Immunofluorescence, Western blot, ELISA
Request SDS/MSDS
To request an SDS/MSDS form for this product, please contact our Technical Support department at:
Technical.Support@LSBio.com
Requested From: United States
Date Requested: 1/15/2025
Date Requested: 1/15/2025