Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
| Catalog Number | Size | Price |
|---|---|---|
| LS-K290-100 | 100 Tests | $415 |
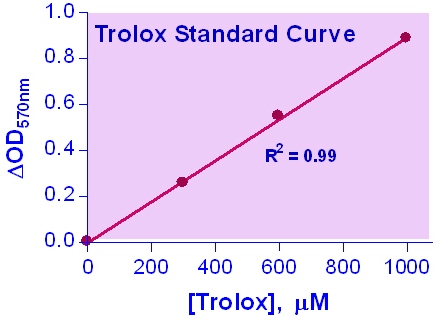
Antioxidant Assay Kit (Colorimetric) - LS-K290
Antioxidant Assay Kit (Colorimetric) - LS-K290
Available for shipment within the USA only
Description:
An ANTIOXIDANT is a molecule capable of slowing or preventing the oxidation of other molecules. Antioxidants protect the cells from damages by reactive oxygen species which are produced in oxidation reactions in the cell. Antioxidants can be small molecules such as glutathione, vitamins, or macromolecules such as catalase, glutathione peroxidase. As oxidative stress contributes to the development of many diseases including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and neurodegeneration, the use of antioxidants in pharmacology is intensively studied. Antioxidants are also widely used as dietary supplements and in industry as preservatives in food, cosmetics, rubber and gasoline. Simple, direct and high-throughput assays for total antioxidant capacity (TAC) find wide applications in research, food industry and drug discovery. This improved assay measures total antioxidant capacity in which Cu2+ is reduced by antioxidant to Cu+. The resulting Cu+ specifically forms a colored complex with a dye reagent. The color intensity at 570nm is proportional to TAC in the sample.
Available for USA Shipment Only
Toll Free North America
 (800) 227-6666
(800) 227-6666
For Research Use Only
Overview
Description:
An ANTIOXIDANT is a molecule capable of slowing or preventing the oxidation of other molecules. Antioxidants protect the cells from damages by reactive oxygen species which are produced in oxidation reactions in the cell. Antioxidants can be small molecules such as glutathione, vitamins, or macromolecules such as catalase, glutathione peroxidase. As oxidative stress contributes to the development of many diseases including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and neurodegeneration, the use of antioxidants in pharmacology is intensively studied. Antioxidants are also widely used as dietary supplements and in industry as preservatives in food, cosmetics, rubber and gasoline. Simple, direct and high-throughput assays for total antioxidant capacity (TAC) find wide applications in research, food industry and drug discovery. This improved assay measures total antioxidant capacity in which Cu2+ is reduced by antioxidant to Cu+. The resulting Cu+ specifically forms a colored complex with a dye reagent. The color intensity at 570nm is proportional to TAC in the sample.
Specifications
Name
Antioxidant Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
Type
Detection/Quantition
Usage
For quantitative determination of total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and evaluation of drug effects on TAC metabolism.
Target
Antioxidant
SampleType
Food and Beverages, Plasma, Serum, Saliva, Urine
Detection
Colorimetric (570 nm Absorbance)
Supplied Components
The following components are supplied with this product.
- Reagent A
- Reagent B
- standard 50 mM Trolox
- (See Datasheet for specific volumes supplied)
Applications
Spectrophotometry (visible)
Equipment
Microplate spectrophotometer (visible)
Conditions
Shipped Ambient, Store at -20°C, 6 months shelf life.
Documents
Restrictions
For research use only. Intended for use by laboratory professionals.
Available for shipment within the USA only
Guarantee
This Assay Kit carries the LSBio 100% Guarantee
Publications (0)
Customer Reviews (0)
Images
Colorimetry
Colorimetry

Colorimetry

Colorimetry

Request SDS/MSDS
To request an SDS/MSDS form for this product, please contact our Technical Support department at:
Technical.Support@LSBio.com
Requested From: United States
Date Requested: 4/14/2025
Date Requested: 4/14/2025










