Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM ABCA7 Antibodies
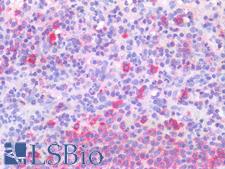
ABCA7 is an ATP-binding cassette transporter that carries various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. This protein has been detected predominantly in myelo-lymphatic tissues with the highest expression in peripheral leukocytes, thymus, spleen, and bone marrow. ABCA7 is involved in ovarian cancer progression, as it has been found to upregulate the TGF-beta signaling pathway resulting in an accelerated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Knockdown of ABCA7 has been shown to decrease the migration of ovarian cancer cells. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, ABCA7 has cytoplasmic and membranous positivity in the brain, bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, and thymus, and in leukocytes and immune cells in tissues throughout the body.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804; Oncol Lett. 2018 Nov;16(5):5868-5874, PMID: 30333865
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
ABCA7
(1)
Application
IHC-P
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Publications
No
(1)

Cancer
Fast Shipping
ABCA7 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results











