Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM ACVRL1 Antibodies
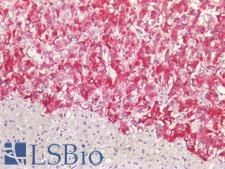
ACVRL1 (Activin A receptor, type II-like 1, activin receptor-like kinase 1) is a type I cell-surface receptor for the TGF-beta superfamily of ligands. ACVRL1 is most highly expressed in human placenta and lung. ACVRL1 protein deficiency and mutations in the gene cause hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2 (HHT2), also known as Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome 2 (ORW2), and also lead to pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. ACVRL1 interaction with low-density lipoprotein (LDL) also implicates it in the early phases of atherosclerosis. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, ACVRL1 has cytoplasmic positivity in the lung, placenta, brain, endocrine tissues, gastrointestinal tissue, gallbladder, pancreas, kidney, testis, smooth muscle, skin, and immune tissues.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804; Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM®. Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD. MIM Number: 600376: 08/22/2019: URL: https://omim.org/; Nature Communications. 7: 13516, PMID: 27869117;
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
ACVRL1
(1)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC-P
(1)
WB
(1)
IF
(1)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(1)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Epitope
aa196-245
(1)
Publications
No
(1)

Cancer
ACVRL1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa196-245) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IF, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results











