Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM APOBEC3B Antibodies
APOBEC3B is a repair gene and cytidine deaminase involved in somatic hypermutation. The deregulation or dysfunction of APOBEC3B and other members of the APOBEC family has been implicated as a direct source of mutagenesis in breast and other cancers. APOBEC3B is upregulated in a number of breast cancers, and this upregulation correlates with a mutation spectrum (kataegis) in these tumors consistent with APOBEC function and may be a simultaneous or upstream consequence of ERBB2 amplification. APOBEC mutation signatures have also been identified in lung cancer, as well as evidence of APOBEC3B upregulation in lung cancer and a correlation between increased expression and worse prognosis in non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), making it an important potential biomarker for the disease. In immunohistochemistry, APOBEC3B has low levels of nuclear positivity in tissues throughout the body, with highest expression in peripheral blood leukocytes and in the spleen, heart, thymus, prostate, ovary, and testes.
References: Genome Biol. 2016; 17: 185, PMID: 27634334; eLife. 2013; 2: e00534, PMID: 23599896; Oncogene. 2018 Jul;37(29):3924-3936, PMID: 29695832; Elife. 2013 Apr 16;2:e00534. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00534, PMID: 23599896; Br J Cancer. 2017 Jun 27; 117(1): 113–123, PMID: 28535155;
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
APOBEC3B
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(1)
ELISA
(1)
IF
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Publications
No
(2)

Cancer
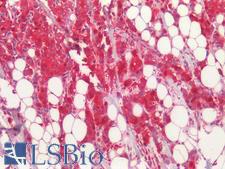
APOBEC3B Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
ELISA, IF, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
0.05 mg/$460

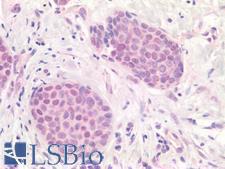
Cancer
Fast Shipping
APOBEC3B Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results










