Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM CALB1 / Calbindin Antibodies
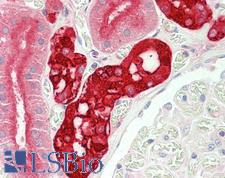
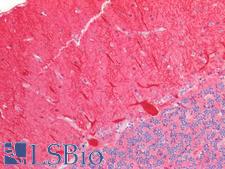
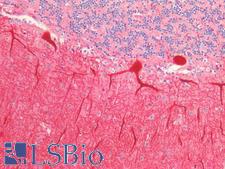
CALB1 (Calbindin) is a protein of the calcium-binding protein superfamily. It functions to buffer the entry of calcium upon glutamate receptor stimulation. In the brain, it is involved in synaptic plasticity. CALB1 has high levels of expression in neurons, and it is associated with sex-specific behavioral regulation and neurobehavioral diseases. Loss of CALB1 in mice results in reduced levels of anxiety, and in humans loss of this protein has been found in patients with Huntington disease. Furthermore, downregulation of CALB1 is seen in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and it is associated with cognitive and memory deficits in AD as well as seizure-prone neurological disorders. In immunohistochemistry, CALB1 has cytoplasmic positivity in Purkinje cells in the cerebellum, in neurons in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus, and in renal tubules.
References: Endocrinology. 2016 May; 157(5): 1967–1979, PMID: 27010449; Nat Med. 2017 Nov;23(11):1377-1383, PMID: 29035369; Cell Rep. 2017 Oct 24;21(4):891-900, PMID: 29069596; Int J Neurosci. 2005 Oct;115(10):1375-82, PMID: 16162445;
3 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(3)
Type
Primary
(3)
Target
CALB1 / Calbindin
(3)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(2)
Hamster
(1)
Pig
(1)
Rabbit
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(3)
WB
(3)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
goat
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(3)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(3)
Format
Unconjugated
(3)
Epitope
aa2-261
(1)
aa3-261
(1)
aa59-72
(1)
Publications
No
(3)

Neuroscience
CALB1 / Calbindin Goat anti-Human Polyclonal (aa59-72) Antibody
Rabbit, Hamster, Pig, Human
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375

Neuroscience
CALB1 / Calbindin Rabbit anti-Mouse Polyclonal (aa3-261) Antibody
Mouse, Rat
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460

Neuroscience
CALB1 / Calbindin Rabbit anti-Rat Polyclonal (aa2-261) Antibody
Rat
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375
Viewing 1-3
of 3
product results











