Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM CCR1 Antibodies
CCR1 (C-C chemokine receptor type 1, CD191) is a member of the beta chemokine receptor family and is a GPCR (G protein-coupled receptor). Knockout studies in mice show that this gene functions in host protection from inflammatory response and is important for susceptibility to viruses and parasites. It is upregulated in macrophages and microglia during the inflammatory response and during myelination in the spinal cord of mice with autoimmune encephalomyelitis. CCR1 is a useful marker for early Alzheimer’s disease, and positivity is strongly correlated with dementia state and is found in plaque-like structures in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. Furthermore, CCR1 is involved in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma and also renal diseases where it regulates myeloid cell kidney infiltration. In immunohistochemistry, CCR1 has positive membranous staining in dendritic cells, monocytes and macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils and lymphocytes.
References: Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan; 37(Database issue): D32–D36, PMID: 18927115; J Neuroinflammation. 2007 May 7;4:14, PMID: 17484785; Am J Pathol 2012;180:1040, PMID: 22203055; Future Med Chem 2011;3:1889, PMID:22023033; Ann Neurol. 2003 Nov;54(5):638-46, PMID: 14595653
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
CCR1
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(1)
ELISA
(1)
ICC
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
goat
(1)
Product Group
GPCR Database Antibodies
(1)
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
Extracellular Domain
(1)
N-Terminus
(1)
Publications
No
(2)

Neuroscience
Fast Shipping
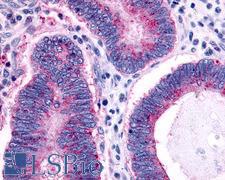
CCR1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Extracellular Domain) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

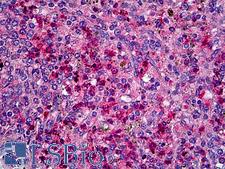
Neuroscience
CCR1 Goat anti-Human Polyclonal (N-Terminus) Antibody
Human
ELISA, ICC, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$515
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results










