Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
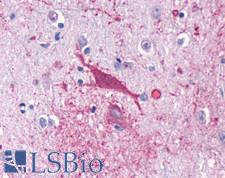
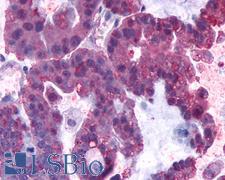
PathPlusTM CNR1 / CB1 Antibodies
CNR1 (CB1, cannabinoid receptor type 1) is a G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor that binds endocannabinoid neurotransmitters and their analogs in the brain. CNR1 functions include regulating cardiac blood supply, inhibiting neuronal excitability in the brain, regulating motor control, and reinforcing drug-seeking behavior in addiction. CNR1 is also an important modulator of anxiety and arousal in response to novel situations; loss of CNR1 has been found to lead to increased object exploration, social interaction and aggression in mice. In immunohistochemistry, CNR1 has membranous positivity in the peripheral and central nervous systems. It is also found on cells in the pituitary, thyroid and adrenal glands, on fat and muscle cells, and in the liver, retina, digestive tract, lungs and kidney.
References: Abood, Mary et al. Cannabinoid receptors: CB1 receptor. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY. 2019, URL: www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=56; Endocrine Reviews. 27 (1): 73–100, PMID: 16306385; PLOS ONE. 6 (11): e26617, PMID: 22069458.
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
CNR1 / CB1
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(2)
Rat
(2)
Bat
(1)
Bovine
(1)
Dog
(1)
Hamster
(1)
Horse
(1)
Monkey
(2)
Pig
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
ICC
(2)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
GPCR Database Antibodies
(2)
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
Cytoplasmic Domain
(1)
Publications
No
(2)

Neuroscience
Fast Shipping
CNR1 / CB1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Mouse, Dog, Bovine, Rat, Pig, Horse, Bat, Human, Monkey
ICC, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Neuroscience
Fast Shipping
CNR1 / CB1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Cytoplasmic Domain) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Hamster, Human, Monkey
ICC, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$440
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results










