Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM FCER2 / CD23 Antibodies
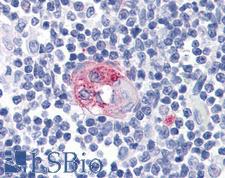
CD23 (FCER2) is a C-type lectin found on the surface of B-cells that acts as a receptor for Immunoglobulin E (IgE). CD23 can be released from the plasma membrane to act as a soluble IgE-binding protein with cytokine functionality. Free CD23 proteins may be cleaved into a range of isoforms of different molecular weights. Functionally, CD23 plays a regulatory role in cell adhesion processes and receptor-mediated feedback loops of the immune response. In immunohistochemistry, CD23 is a membranous marker for activated B-cells, macrophages, some follicular dendritic cells in germinal centers and a subset of B cells in the mantle zone of lymphoid tissues. It is positive in small lymphocytic lymphomas and B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia, but not mantle cell lymphomas.
References: Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Oct; 162(1): 12–23, PMID: 20831712; Eur J Immunol. 1993 Sep;23(9):2066-71, PMID: 8370388
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
FCER2 / CD23
(1)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-Fr
(1)
IHC-P
(1)
Flo
(1)
Host
mouse
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(1)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(1)
Isotype
IgG1
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
Clone
EBVCS2
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Publications
No
(1)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
FCER2 / CD23 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (EBVCS2) Antibody
Human
Flo, IHC, IHC-Fr, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results











