Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
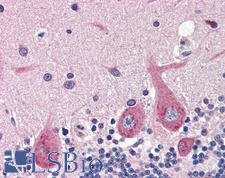
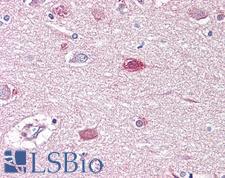
PathPlusTM GAD1 / GAD67 Antibodies
GAD1 (Glutamate decarboxylase 1, GAD67, brain, 67kDa) is a glutamic acid decarboxylase that functions to catalyze gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) synthesis from L-glutamic acid. It is an autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes, and mutation or deficiency in GAD1 results in pyridoxine-dependent seizures. GAD1 mutation or dysregulation are also thought to contribute to improper neuronal activity and connection formation during development and may be involved in cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Separately, epigenetic upregulation of GAD1 leads to an increase in aggressive characteristics in metastatic brain cancers. GAD1 has highest positivity in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum and basal ganglia in the brain, with limited expression in the testes, parathyroid and a few other tissues.
References: PLoS One. 2017 Jan 25;12(1):e0170805, PMID: 28122016; Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 19;8(1):15470, PMID: 30341396; Cancer Res. 2017 Jun 1;77(11):2844-2856, PMID: 28400476; Neurology. 2000 Jul 25;55(2):309-11, PMID: 10908915
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
GAD1 / GAD67
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(2)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(2)
Peptide-ELISA
(2)
Host
rabbit
(1)
goat
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
aa471-520
(1)
aa526-537
(1)
Publications
No
(2)

Neuroscience
GAD1 / GAD67 Goat anti-Human Polyclonal (aa526-537) Antibody
Mouse, Human
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$485

Neuroscience
GAD1 / GAD67 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa471-520) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results











