Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM GCG / Glucagon Antibodies
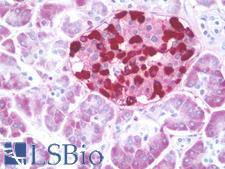
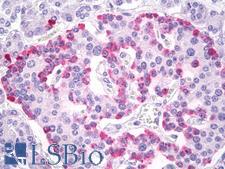
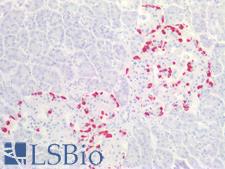
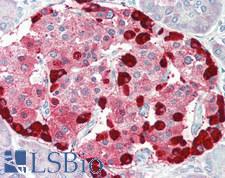
Glucagon (GCG, GLP-1) is a peptide hormone secreted by pancreatic alpha cells. It plays a key role in glucose metabolism and homeostasis, and regulates blood glucose by increasing gluconeogenesis and decreasing glycolysis. It is a counter-regulatory hormone of insulin, raises plasma glucose levels in response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia. In diabetes, it plays an important role in initiating and maintaining hyperglycemic conditions. Glucagon also has important functions in nutrient homeostasis, enhancing nutrient assimilation through enhanced gastrointestinal function, as well as increasing nutrient disposal. It also inhibits gastric emptying in humans, which may lead to increased gastric distension and contribute to satiety by causing a sensation of fullness. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, GCG has cytoplasmic positivity in cells in islets of Langerhans in the pancreas.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804;
4 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(4)
Type
Primary
(4)
Target
GCG / Glucagon
(4)
Reactivity
Human
(4)
Mouse
(2)
Rat
(1)
Bovine
(1)
Dog
(1)
Pig
(1)
Sheep
(1)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-P
(4)
WB
(4)
Flo
(2)
ICC
(1)
IF
(2)
Host
rabbit
(4)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(4)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(4)
Format
Unconjugated
(4)
Epitope
Internal
(1)
aa119-148
(1)
aa25-54
(1)
Publications
No
(4)

Cancer
GCG / Glucagon Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa119-148) Antibody
Human
Flo, IF, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
200 µl/$460

Cancer
GCG / Glucagon Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa25-54) Antibody
Mouse, Human
Flo, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
200 µl/$460

Cancer
GCG / Glucagon Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Mouse, Dog, Sheep, Bovine, Rat, Pig, Human
ICC, IF, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

Cancer
GCG / Glucagon Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375
Viewing 1-4
of 4
product results










