Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM MOG Antibodies
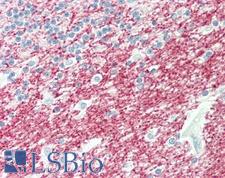
MOG (Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein) is a membrane protein found on the cell surface of oligodendrocyte and the outermost surface of myelin sheaths. It functions in the myelination of nerves in the central nervous system, and is involved in maintaining myelin sheath structural integrity and in cellular communication. Some individuals with multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD) produce autoantibodies to MOG, which may contribute to flares of inflammatory demyelination in the central nervous system. In immunohistochemistry, MOG is only found in the central nervous system, and has membranous positivity on oligodendrocytes.
References: Neurology. Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation. 2016. 3(5), DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000257; Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2018; 11, PMID: 29623106
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
MOG
(1)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(1)
ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(1)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Epitope
aa163-174
(1)
Publications
No
(1)

Neuroscience
MOG Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa163-174) Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results











