Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM PARK7 / DJ-1 Antibodies
PARK7 (Protein deglycase DJ-1, Parkinson disease protein 7) is a peptidase of the C56 family that is responsible for inhibiting alpha-synuclein aggregation. It helps protect cells against oxidative stress and cell death. It is also required for correct mitochondrial morphology and function and for autophagy of dysfunctional mitochondria. In the brain, PARK7 regulates the inflammatory response in astrocytes and may regulate lipid raft-dependent endocytosis in astrocytes and neuronal cells. PARK7 is implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease, where it is upregulated in reactive astrocytes. Mutations in PARK7 are a direct cause of early-onset recessive forms of the disease. Such mutations disrupt lipid raft assembly and lead to impaired glutamate uptake and are associated with Lewy body pathology. Loss of function or knockout of PARK7 also leads to a limited ability of astrocytes to protect neurons from neurotoxicity. In immunohistochemistry, PARK7 has cytoplasmic and nuclear positivity in most tissues throughout the body.
References: Mol. Genet. 2013;22:4805–4817, PMID: 23847046; J. Neurochem. 2011;117:375–387, PMID: 21219333; Trends Neurosci. 2017 Jun; 40(6): 358–370, PMID: 28527591; Brain. 2016. 139 (6), 1680–1687:10.1093/brain/aww080
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
PARK7 / DJ-1
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(1)
Bovine
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(2)
ICC
(1)
IF
(1)
Host
mouse
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Isotype
IgG1
(1)
IgG1,k
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(2)
Clone
3E8
(1)
4H4
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Publications
No
(2)

Neuroscience
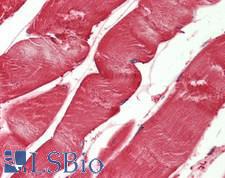
PARK7 / DJ-1 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (4H4) Antibody
Mouse, Bovine, Human
ICC, IF, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

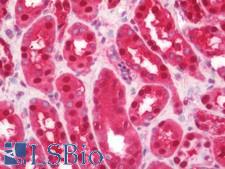
Neuroscience
PARK7 / DJ-1 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (3E8) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results











