Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM PDCD4 Antibodies
PDCD4 is a protein that localizes to the nucleus in proliferating cells. PDCD4 expression is modulated by cytokines in natural killer and T cells, and it is thought to play a role in apoptosis. PDCD4 inhibits the translation initiation factor E1F4A, and phosphorylation by AKT causes nuclear translocation of PDCD4 and also decreases the ability of PDCD4 to interfere with the transactivation of AP-1 responsive promoter by c-JUN. Loss of PDCD4 expression in human lung carcinoma correlates with tumor progression and prognosis. In immunohistochemistry, PDCD4 has nuclear and cytoplasmic positivity in a majority of tissues throughout the body.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804;
4 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(4)
Type
Primary
(4)
Target
PDCD4
(4)
Reactivity
Human
(4)
Mouse
(3)
Rat
(3)
Bat
(1)
Bovine
(1)
Chicken
(1)
Dog
(1)
Goat
(1)
Hamster
(1)
Horse
(1)
Monkey
(1)
Pig
(1)
Rabbit
(1)
Application
IHC
(4)
IHC-P
(4)
WB
(3)
ELISA
(2)
Peptide-ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(3)
mouse
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(4)
Isotype
IgG
(3)
IgG1,k
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(3)
Clone
K4C1
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(4)
Epitope
aa1-469
(1)
aa33-82
(1)
Publications
No
(3)
Yes
(1)

Cancer
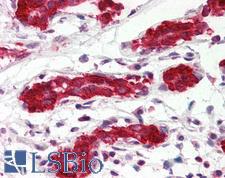
PDCD4 Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (aa1-469) (K4C1) Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375

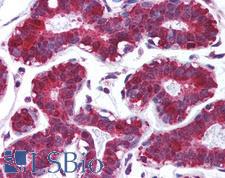
Cancer
PDCD4 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
ELISA, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375

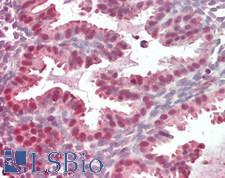
Cancer
PDCD4 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa33-82) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, Peptide-ELISA
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375

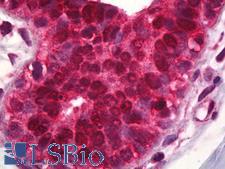
Cancer
PDCD4 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Chicken, Bovine, Rabbit, Mouse, Goat, Dog, Rat, Hamster, Pig, Horse, Bat, Human, Monkey
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375
Viewing 1-4
of 4
product results











