Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM S100A6 / Calcyclin Antibodies
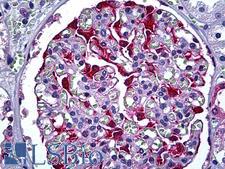
S100A6 (Calcyclin) is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are found in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, where they modulate cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100A6 may stimulate Ca2+-dependent insulin release, prolactin secretion, and exocytosis, and it may also alter stress responses. In the brain, it is primarily expressed in neurons in the amygdala and entorhinal cortex, as well as in some astrocytes. S100A6 is overexpressed in neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, upregulation in astrocytes). Furthermore, chromosomal rearrangements and altered expression of this gene have been implicated in melanoma. In immunohistochemistry, S100A6 has cytoplasmic and nuclear positivity in most tissues throughout the body.
References: PLoS One. 2017; 12(1): e0169760, PMID: 28068373; J Comp Neurol. 1999 Feb 8; 404(2):235-57, PMID: 9934997; Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol. 2010; 2010: 720958, PMID: 20862335; Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology. 61( 8). 2002. 736–744, DOI:10.1093/jnen/61.8.736; Front. Neurosci., 2019, DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00463;
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
S100A6 / Calcyclin
(1)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(1)
WB
(1)
ELISA
(1)
IF
(1)
Host
mouse
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(1)
Isotype
IgG1,k
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
Clone
6B5
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Publications
No
(1)

Neuroscience
S100A6 / Calcyclin Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (6B5) Antibody
Human
ELISA, IF, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results











