order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
APH / APEH
acylaminoacyl-peptide hydrolase
APH / APEH is the enzyme acylpeptide hydrolase, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of the terminal acetylated amino acid preferentially from small acetylated peptides. The acetyl amino acid formed by this hydrolase is further processed to acetate and a free amino acid by an aminoacylase. This gene is located within the same region of chromosome 3 (3p21) as the aminoacylase gene, and deletions at this locus are also associated with a decrease in aminoacylase activity. The acylpeptide hydrolase is a homotetrameric protein of 300 kDa with each subunit consisting of 732 amino acid residues. It can play an important role in destroying oxidatively damaged proteins in living cells. Deletions of this gene locus are found in various types of carcinomas, including small cell lung carcinoma and renal cell carcinoma.
| Gene Name: | acylaminoacyl-peptide hydrolase |
| Family/Subfamily: | Protease , Serine S9C |
| Synonyms: | APEH, Acylpeptide hydrolyase, Acyl-peptide hydrolase, ACPH, DNF15S2, D3F15S2, AARE, Acylaminoacyl-peptidase, OPH, Oxidized protein hydrolase, APH, D3S48E |
| Target Sequences: | NM_001640 NP_001631.3 P13798 |
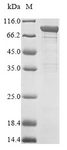
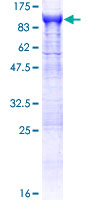
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.









