order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
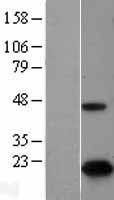
CDKN2A
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A
Capable of inducing cell cycle arrest in G1 and G2 phases. Acts as a tumor suppressor. Binds to MDM2 and blocks its nucleocytoplasmic shuttling by sequestering it in the nucleolus. This inhibits the oncogenic action of MDM2 by blocking MDM2-induced degradation of p53 and enhancing p53-dependent transactivation and apoptosis. Also induces G2 arrest and apoptosis in a p53-independent manner by preventing the activation of cyclin B1/CDC2 complexes. Binds to BCL6 and down-regulates BCL6-induced transcriptional repression. Binds to E2F1 and MYC and blocks their transcriptional activator activity but has no effect on MYC transcriptional repression. Binds to TOP1/TOPOI and stimulates its activity. This complex binds to rRNA gene promoters and may play a role in rRNA transcription and/or maturation. Interacts with NPM1/B23 and promotes its polyubiquitination and degradation, thus inhibiting rRNA processing. Interacts with COMMD1 and promotes its 'Lys63'-linked polyubiquitination. Interacts with UBE2I/UBC9 and enhances sumoylation of a number of its binding partners including MDM2 and E2F1. Binds to HUWE1 and represses its ubiquitin ligase activity. May play a role in controlling cell proliferation and apoptosis during mammary gland development. Isoform 6 may be involved in regulation of autophagy and caspase-independent cell death; the short-lived mitochondrial isoform is stabilized by C1QBP.
| Gene Name: | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A |
| Synonyms: | CDKN2A, ARF, Cdk4 inhibitor, CDK4 inhibitor p16-INK4, INK4, INK4A, Multiple tumor suppressor 1, MTS-1, MTS1, p16-INK4, p16-INK4A, p16INK4, p19, p14, p16, p16 INK4A, p16INK4A, p14ARF, TP16, CDK4I, CDKN2, CMM2, MLM, p19ARF |
| Target Sequences: | NM_000077 NP_000068.1 P42771 |
Publications (36)

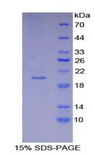


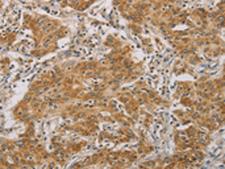













If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.









