order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
F13A1 / Factor XIIIa
coagulation factor XIII, A1 polypeptide
F13A1 / Factor XIIIa is the coagulation factor XIII A subunit. Coagulation factor XIII is the last zymogen to become activated in the blood coagulation cascade. Plasma factor XIII is a heterotetramer composed of 2 A subunits and 2 B subunits. The A subunits have catalytic function, and the B subunits do not have enzymatic activity and may serve as plasma carrier molecules. Platelet factor XIII is comprised only of 2 A subunits, which are identical to those of plasma origin. Upon cleavage of the activation peptide by thrombin and in the presence of calcium ion, the plasma factor XIII dissociates its B subunits and yields the same active enzyme, factor XIIIa, as platelet factor XIII. This enzyme acts as a transglutaminase to catalyze the formation of gamma-glutamyl-epsilon-lysine crosslinking between fibrin molecules, thus stabilizing the fibrin clot. It also crosslinks alpha-2-plasmin inhibitor, or fibronectin, to the alpha chains of fibrin. Factor XIII deficiency is classified into two categories: type I deficiency, characterized by the lack of both the A and B subunits; and type II deficiency, characterized by the lack of the A subunit alone. These defects can result in a lifelong bleeding tendency, defective wound healing, and habitual abortion.
| Gene Name: | coagulation factor XIII, A1 polypeptide |
| Synonyms: | F13A1, Coagulation factor XIIIa, Factor XIIIa, Fibrinoligase, FSF, A subunit, Transglutaminase. plasma, Transglutaminase A chain, F13A, TGASE |
| Target Sequences: | NM_000129 NP_000120.2 P00488 |
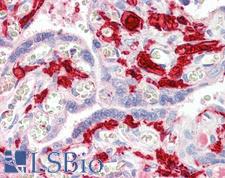
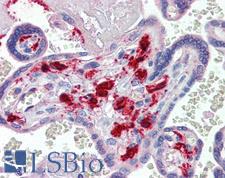
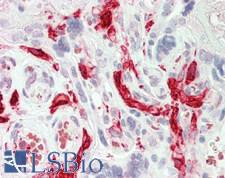

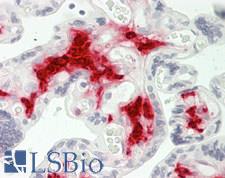
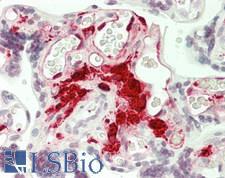
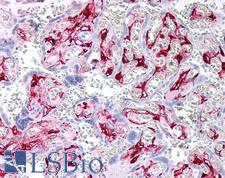
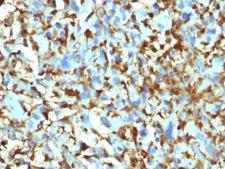
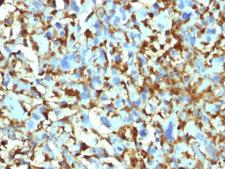

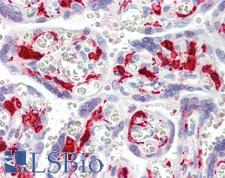
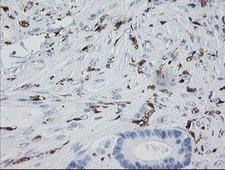
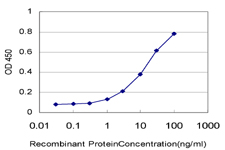
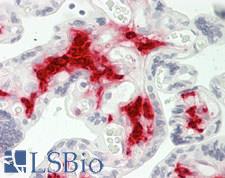
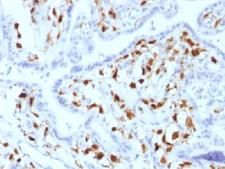
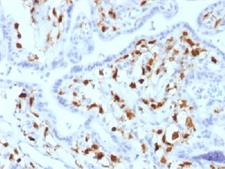
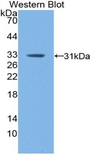

If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.












