Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM ABCA1 Antibodies
ABCA1 (ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 1, CERP) is a transporter protein that modulates phospholipid homeostasis, cellular cholesterol. ABCA1 is necessary for proper cholesterol metabolism and transport in the central nervous system. It has highest expression in the liver, adipose tissue and the small intestine, and is otherwise found throughout the body. Mutations in ABCA1 lead to the rare Tangier’s disease, described by a massive reduction in high density lipoprotein in the body and which can lead to neuropathy and cardiovascular disease. Downregulation of ABCA1 leads to atherogenesis through a disruption of cholesterol transport within cells and is a factor in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and macular degeneration. Upregulation of ABCA1 has been found to reduce amyloid deposition in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. In immunohistochemistry of normal tissue, ABCA1 has membranous and cytoplasmic positivity in tissues throughout the body.
References: Cell Metabolism. 17 (4): 549–61, PMID: 23562078; J Clin Invest. 2008;118(2):671–682, DOI: doi.org/10.1172/JCI33622; J Neurosci. 2009 Mar 18; 29(11): 3579–3589, PMID: 19295162
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
ABCA1
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Mouse
(2)
Rat
(1)
Chicken
(1)
Dog
(1)
Hamster
(1)
Mustelid
(1)
Pig
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(2)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
aa100-150
(1)
aa1100-1300
(1)
Publications
No
(2)

Neuroscience
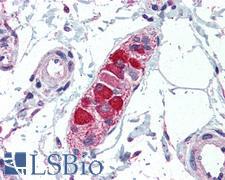
ABCA1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa1100-1300) Antibody
Chicken, Mouse, Dog, Rat, Hamster, Pig, Mustelid, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
0.1 ml/$375

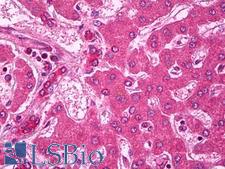
Neuroscience
ABCA1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa100-150) Antibody
Mouse, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$375
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results











