Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM GLP2R Antibodies
Glucagon-like peptide 2 receptor (GLP2R) is closely related to the Glucagon Receptor and to the GLP1 Receptor. The glucagon-like peptides (GLP-1 and GLP-2) are proglucagon-derived peptides cosecreted from gut endocrine cells in response to nutrient ingestion. GLP2R is mediated by the GLP-2 receptor expressed on subsets of enteric nerves and enteroendocrine cells in the stomach and small and large intestine. Activation of GLP2R signaling promotes expansion of the mucosal epithelium indirectly via activation of growth and anti-apoptotic pathways. GLP2R, through its ligand glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP2), has been shown to prevent intestinal hypoplasia resulting from total parenteral nutrition.
References: The UniProt Consortium. Nucleic Acids Res. 47: D506-515 (2019); Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D733-45, PMID:26553804
2 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(2)
Type
Primary
(2)
Target
GLP2R
(2)
Reactivity
Human
(2)
Guinea pig
(1)
Monkey
(1)
Application
IHC
(2)
IHC-P
(2)
WB
(1)
ICC
(1)
IF
(1)
IP
(1)
Host
rabbit
(2)
Product Group
Alzheimer's Disease
(2)
GPCR Database Antibodies
(2)
PathPlus Neuro
(2)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(2)
Format
Unconjugated
(2)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
N-Terminus
(1)
Publications
No
(1)
Yes
(1)

Neuroscience
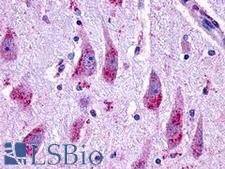
GLP2R Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (N-Terminus) Antibody
Guinea pig, Human, Monkey
ICC, IF, IHC, IHC-P, IP, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$440

Neuroscience
Fast Shipping
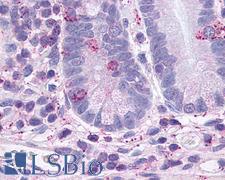
GLP2R Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-2
of 2
product results











