Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM KCNJ2 / Kir2.1 Antibodies
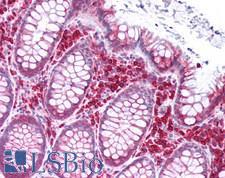
KCNJ2 (Kir2.1 inward-rectifier potassium ion channel) is a potassium ion channel protein that maintains resting membrane potential and regulates cell excitability. It plays an important role in neural and craniofacial development. It is highly expressed in the hippocampus, nucleus accumbens, putamen and caudate in the brain as well as in skeletal muscle, and is central to the inward-rectifier current (IK1) that controls cardiac excitability in human ventricular muscle. Mutations in KCNJ2 affect neuronal excitability and are associated with Autism, short-QT syndrome and Andersen-Tawil syndrome. In immunohistochemistry, KCNJ2 has cytoplasmic positivity in most tissues throughout the body.
References: Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00076; Heart Rhythm. 2005 Mar;2(3):316-24, PMID: 15851327; Cardiovascular Research. 2012. 93 (4): 666–673, DOI:10.1093/cvr/cvr329; J Physiol. 2016 Jun 15;594(12):3245-70, PMID: 26864374
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
KCNJ2 / Kir2.1
(1)
Reactivity
Human
(1)
Mouse
(1)
Rat
(1)
Application
IHC-P
(1)
WB
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Neuro
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Epitope
Internal
(1)
Publications
No
(1)

Neuroscience
KCNJ2 / Kir2.1 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Internal) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results











