Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM LPAR2 / EDG4 Antibodies
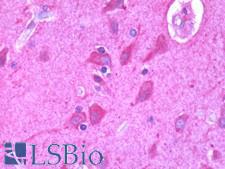
LPAR2 is a receptor for lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), a mediator of diverse cellular activities. It is coupled to the G(i)/G(o), G(12)/G(13), and G(q) families of heteromeric G proteins. It plays an important role in the phospholipase C-beta (PLC-beta) signaling pathway, and it stimulates phospholipase C (PLC) activity in a manner that is independent of RALA activation. LPAR2 is important for vascular development, and loss of this protein results can result in vascular defects including frontal cerebral hematomas. Furthermore, loss of LPAR2 signaling in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (in mice) promotes disease progression. In immunohistochemistry, LPAR2 has membranous and cytoplasmic positivity in most tissues throughout the body.
References: Neuron. 2015 Feb 18;85(4):669-82, PMID: 25695267; Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2017 Jun 2;5(1):42, PMID: 28578681
1 PathPlusTM Antibody
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(1)
Type
Primary
(1)
Target
LPAR2 / EDG4
(1)
Application
IHC
(1)
IHC-P
(1)
ICC
(1)
Host
rabbit
(1)
Product Group
GPCR Database Antibodies
(1)
PathPlus Cancer
(1)
Clonality
polyclonal pc
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(1)
Epitope
Cytoplasmic Domain
(1)
Publications
No
(1)

Cancer
Fast Shipping
LPAR2 / EDG4 Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (Cytoplasmic Domain) Antibody
ICC, IHC, IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-1
of 1
product results











