Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
PathPlusTM NOS2 / iNOS Antibodies
NOS2 (iNOS, nitric oxide synthase 2, inducible) is a synthase for nitric oxide, a reactive free radical and messenger molecule that acts a biologic mediator in neurotransmission and antimicrobial/anti-cancer processes. In macrophages, nitric oxide mediates tumoricidal and bactericidal actions. It also has nitrosylase activity and mediates cysteine S-nitrosylation of cytoplasmic target proteins such COX2. In immunohistochemistry, NOS2 antibodies may be used to characterize epithelial injury and cells undergoing apoptosis in sites of inflammation. NOS2 may be useful in diagnosing liver diseases, as NOS2 has high expression in a number of pathologies and is involved in the etiology of liver fibrosis. Furthermore, antibodies to NOS2 may have utility in cancer: elevated levels of NOS2 have been found in cancers of the lung, colon, and prostate as well as in melanoma, glioblastoma and oral dysplasia, and high levels of NOS2 in cancers are generally correlated with poor prognosis. In normal tissue, NOS2 is positive in the gastrointestinal tract, appendix and urinary bladder.
References: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90 (8): 3491–5, PMID: 7682706; Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000 Nov; 90(5):624-9, PMID: 11077387; Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Dec; 6(12):4768-75, PMID: 11156233; Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2014 May; 19(3): e242–e247, PMID: 24316703; Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009 Jan;133(1):97-100, PMID: 19123745; Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015 Dec; 21(4): 319–325, PMID: 26770919;
4 PathPlusTM Antibodies
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(4)
Type
Primary
(4)
Target
NOS2 / iNOS
(4)
Reactivity
Human
(3)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-Fr
(1)
IHC-P
(4)
WB
(2)
Flo
(1)
ELISA
(1)
Host
rabbit
(3)
mouse
(1)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(4)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(1)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
IgG1
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(1)
polyclonal pc
(3)
Clone
4E5
(1)
K13-A
(1)
Format
Unconjugated
(4)
Epitope
90-170 aa
(1)
aa997-1058
(1)
Publications
No
(3)
Yes
(1)

Cancer
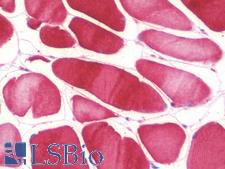
NOS2 / iNOS Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (aa997-1058) (4E5) Antibody
Human
ELISA, Flo, IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µg/$375

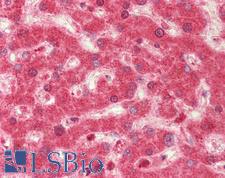
Cancer
NOS2 / iNOS Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (K13-A) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-Fr, IHC-P
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375

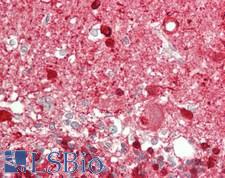
Cancer
NOS2 / iNOS Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (90-170 aa) Antibody
Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µg/$375

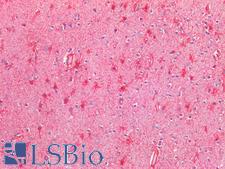
Cancer Pathology
Cancer
Fast Shipping
NOS2 / iNOS Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-4
of 4
product results











