order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
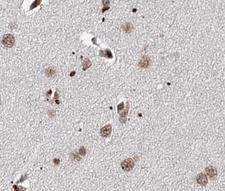
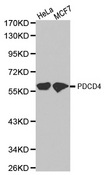
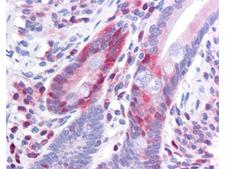
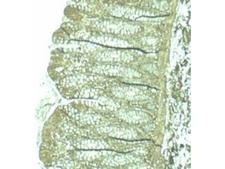
PDCD4
programmed cell death 4 (neoplastic transformation inhibitor)
This gene encodes a protein localized to the nucleus in proliferating cells. Expression of this gene is modulated by cytokines in natural killer and T cells. The gene product is thought to play a role in apoptosis but the specific role has not yet been determined. Two transcripts encoding different isoforms have been identified. PDCD4 inhibits the translation initiation factor E1F4A. Phosphorylation by AKT causes nuclear translocation of PDCD4 and also decreases the ability of PDCD4 to interfere with the transactivation of AP-1 responsive promoter by c-JUN. Loss of PDCD4 expression in human lung carcinoma correlates with tumor progression and prognosis.
| Gene Name: | programmed cell death 4 (neoplastic transformation inhibitor) |
| Family/Subfamily: | Apoptosis |
| Synonyms: | PDCD4, H731, Nuclear antigen H731-like, Nuclear antigen H731, Protein 197/15a |
| Target Sequences: | NM_014456 NP_055271.2 Q53EL6 |
Publications (5)
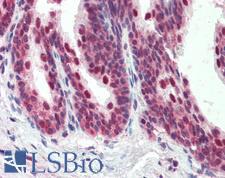
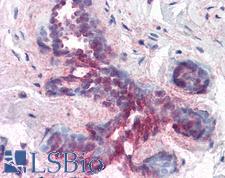
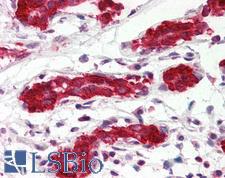
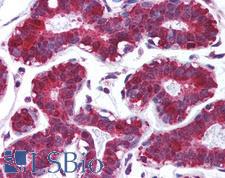
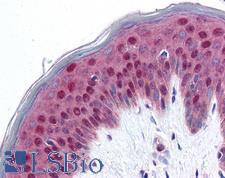
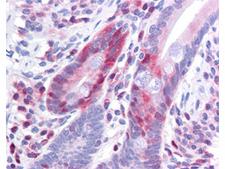


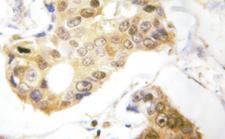
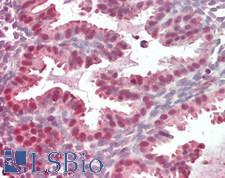
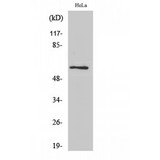
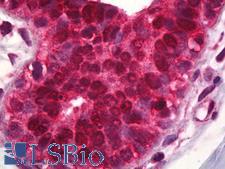
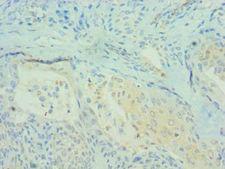
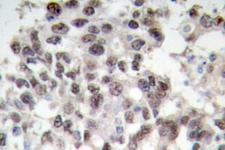
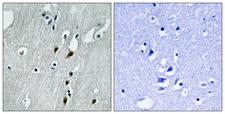

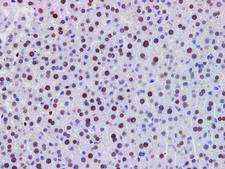

If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.












