Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
Products
Antibodies
ELISA and Assay Kits
Research Areas
Infectious Disease
Resources
Purchasing
Reference Material
Contact Us
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
Login
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
Registration enables users to use special features of this website, such as past
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Quick Order
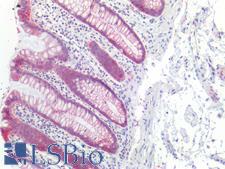
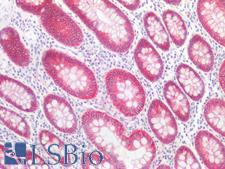
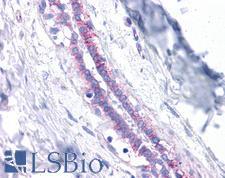
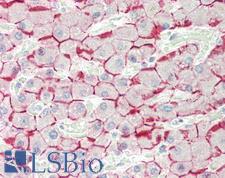
PathPlusTM CDH1 / E Cadherin Antibodies
E-cadherin (CDH1) is a calcium-depending glycoprotein that is involved in cell to cell adhesion and is expressed on the surface of epithelial tissues. Loss of e-cadherin is associated with decreased cell adhesion, increased cellular motility, invasion and poor prognosis in carcinomas, particularly lobular carcinomas of the breast. In immunohistochemistry, e-cadherin is positive in normal breast ducts, the epithelium of the GI tract, hepatocytes and bile ducts. In cancer, it is positive in breast ductal carcinoma (but not lobular), esophageal adenocarcinoma and squamous carcinoma, and bladder transitional cell carcinoma.
References: Eur J Cancer 2000, 36:1607; Cell. 2015 Oct 8;163(2):506-19, PMID: 26451490; Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Jul 27;19(1):86, PMID: 28750639; Oncotarget 2017 Jan; 8.1; 16445-16455, PMID: 28147315; Oncotarget. 2016 Nov; 7.49; 80655-80663, PMID: 27811364;
9 PathPlusTM Antibodies
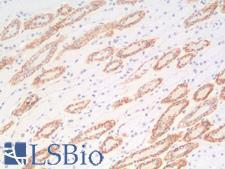
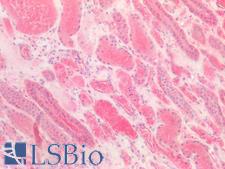
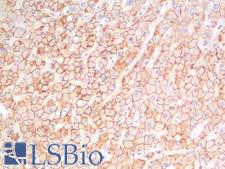
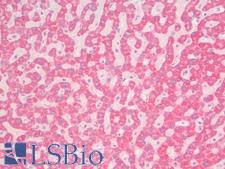
☰ Filters
Products
Antibodies
(9)
Type
Primary
(9)
Target
CDH1 / E Cadherin
(9)
Reactivity
Human
(7)
Mouse
(2)
Rat
(3)
Bovine
(1)
Dog
(1)
Monkey
(1)
Pig
(1)
Rabbit
(1)
Zebrafish
(1)
Application
IHC
(3)
IHC-P
(9)
WB
(5)
Flo
(1)
ELISA
(2)
ICC
(1)
IF
(2)
IP
(1)
Host
rabbit
(6)
mouse
(3)
Product Group
PathPlus Cancer
(9)
PathPlus Cancer Pathology
(9)
Isotype
IgG
(1)
IgG1
(1)
IgG1,k
(1)
Clonality
monoclonal mc
(2)
polyclonal pc
(6)
recombinant monoclonal rmc
(1)
Clone
813CT11.1.3
(1)
rCDH1/1525
(1)
Format
Concentrated
(1)
Unconjugated
(9)
Epitope
C-Terminus
(1)
N-Terminus
(1)
aa503-552
(1)
Publications
No
(9)

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CDH1 / E Cadherin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (C-Terminus) Antibody
Zebrafish, Pig, Rat, Rabbit, Dog, Bovine, Human, Monkey
Flo, ICC, IF, IHC-P, IP, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CDH1 / E Cadherin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (N-Terminus) Antibody
Mouse, Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
50 µl/$460

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CDH1 / E Cadherin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal (aa503-552) Antibody
Rat, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CDH1 / E Cadherin Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (813CT11.1.3) Antibody
Mouse, Human
IHC, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µl/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CDH1 / E Cadherin Mouse anti-Human Recombinant Monoclonal (rCDH1/1525) Antibody
Human
IF, IHC-P, WB
Unconjugated
100 µg/$525

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CDH1 / E Cadherin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC-P
Unconjugated
100 µg/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
CDH1 / E Cadherin Mouse anti-Human Monoclonal (Concentrated) Antibody
Human
ELISA, IHC-P
Unconjugated, Concentrated
0.05 ml/$375

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
Fast Shipping
CDH1 / E Cadherin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395

Cancer Pathology
Cancer
Fast Shipping
CDH1 / E Cadherin Rabbit anti-Human Polyclonal Antibody
IHC-P
Unconjugated
50 µg/$395
Viewing 1-9
of 9
product results











