order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Location
Corporate Headquarters
Vector Laboratories, Inc.
6737 Mowry Ave
Newark, CA 94560
United States
Telephone Numbers
Customer Service: (800) 227-6666 / (650) 697-3600
Contact Us
Additional Contact Details
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Forgot password?
order histories, retained contact details for faster checkout, review submissions, and special promotions.
Biotin
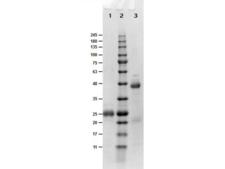
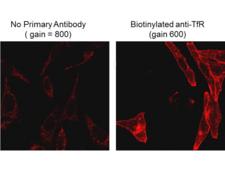
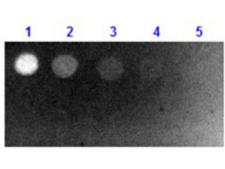
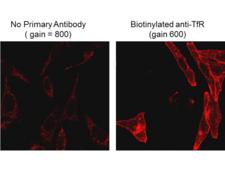
Biotin is widely used throughout the biotechnology industry to conjugate proteins for biochemical assays. Biotin's small size means the biological activity of the protein will most likely be unaffected. This process is called biotinylation. Because both streptavidin and avidin bind biotin with high affinity (Kd of 10-14 mol/l to 10-15 mol/l) and specificity, biotinylated proteins of interest can be isolated from a sample by exploiting this highly stable interaction. The sample is incubated with streptavidin/avidin beads, allowing capture of the biotinylated protein of interest. Any other proteins binding to the biotinylated molecule will also stay with the bead and all other unbound proteins can be washed away. However, due to the extremely strong streptavidin-biotin interaction, very harsh conditions are needed to elute the biotinylated protein from the beads (typically 6M guanidine HCl at pH 1.5), which often will denature the protein of interest. To circumvent this problem, beads conjugated to monomeric avidin can be used, which has a decreased biotin-binding affinity of ~10-8 mol/l, allowing the biotinylated protein of interest to be eluted with excess free biotin. ELISAs often make use of biotinylated secondary antibodies against the antigen of interest, followed by a detection step using streptavidin conjugated to a reporter molecule, such as horseradish peroxidase or alkaline phosphatase.
Biotin Target Details
| Target Name: | Biotin |
Publications (1)
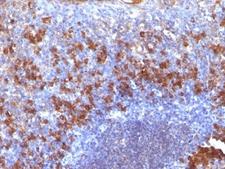
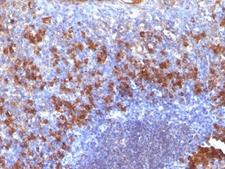
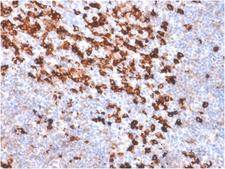
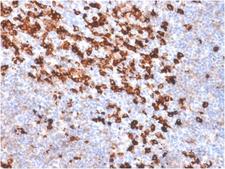
If you do not find the reagent or information you require, please contact Customer.Support@LSBio.com to inquire about additional products in development.